Stress-Strain curve
Stress-Strain curve
- Region OA in the graph is linear. Hook's law is obeyed. Solid behaves like elastic body. Point A is the elastic limit.
- In region AB, stress & strain are not proportional. But body can regain its original shape & size when the load is removed.
- Point B is called yield point & corresponding stress is called yield strength.
- When load is removed at point C between region B&D, body does not regain original dimension.
- Even stress is zero, strain is not zero in the region BD. Point C is called set point.
- At point C the material is in a permanent set & the deformation is called Plastic deformation.
- Point D is called ultimate stress. At this point wire becomes thin.
- Point E represents break point. Where the body physically breaks.
- If point D & E are very close, material is said to be brittle.
- If point D & E are far apart, material is said to be ductile.
Ultimate stress - It is defined as the maximum stress that
can applied be to a material; so that it remain withstand.
Breaking stress - It is defined as the maximum stress at which
wire under stress physically breaks.
Working stress - It is the stress which is considered as the
allowable stress for design purpose.
working stress should always be smaller than Ultimate stress.
Factor of safety - It is the ratio of ultimate stress to working stress.

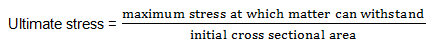



Comments
Post a Comment