Stress & Strain
Deforming force - An applied external force which changes shape & size of the body; known as deforming force.
The change of shape & size of
the body after application of deforming force is called deformation.
Restoring force - When a body is subjected to deforming
force a restoring force is developed in the body. This restoring force is equal
in magnitude but opposite in direction of deforming force.
Elastic body - If a
body regains its original size & shape after removable of deforming force
then the body is called elastic body.
E.g. spring, rubber,
balloons, Jelly, tennis ball etc.
Elasticity - It is defined as a property of a body through
which body tends to regain its original size & shape on removal of deforming
force.
Plastic body - If a body does not regain its original size
& shape after removable of deforming force then the body is called plastic
body.
E.g. wax, putty, toys made of clay etc.
Plasticity - It is defined as a property of a body because
of which body does not regain its original size & shape on removal of
deforming force.
Stress - The internal restoring force per unit area of the
body is called stress.
Unit- N/m2
Strain - It is defined as the ratio of change in dimension
to the original dimension of the body.
i.e.;
It is a unit less quantity.
Longitudinal stress
Tensile stress
If a wire suspended from a rigid support having length "L" and mass "m" is attached to its free end then the downward force "mg" acts on a wire and wire elongates by "l". If "r" is radius of wire then its cross sectional area is πr².
Compressive stress
If the body is compressed after application of deforming force then the stress is called Compressive stress.
Tensile stress & Compressive stress are also termed as longitudinal stress.
Tensile stress & Compressive stress are also termed as longitudinal stress.
Longitudinal strain
Tensile strain- It is defined as the ratio of increase in length of wire to the original length of wire.
Compressive strain- It is defined as the ratio of decrease in length of wire to the original length of wire.
Tensile strain & Compressive strain are also termed as longitudinal strain.
Volume stress
If a balloon has volume "V" at atmospheric pressure "P" & it is compressed with additional pressure "dp" then its volume decreases as shown in figure.
Shearing stress or tangential stress
If two equal and opposite deforming forces are applied parallel to the cross sectional area of cylinder as shown in figure below then there is a relative displacement between the opposite faces of cylinder.
The restoring force per unit area developed due to applied tangential force is called as
Shearing stress or tangential stress.Shearing strain
It is defined as the ratio of relative displacement between two layers under the action of force to the distance between the two layers.
It is a unit less quantity.




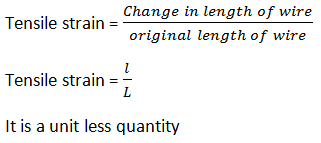







Comments
Post a Comment