Accuracy & Precision
Accuracy & Precision
Difference between accuracy and precision
Significant figure/digit- The digit in a measurement which is trustworthy; are called significant figures
Accuracy -
Precision - Precision refers to the closeness of two or more readings taken by a measuring instrument.
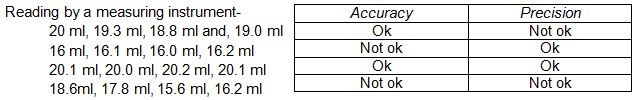
The above two statement will get a clear view from the following example-
The above two statement will get a clear view from the following example-
let the true value of
tea in a cup is 20 ml.
Difference between accuracy and precision
Accuracy
|
Precision
|
Accuracy is the agreement of
the result of measurement with true value. It is an ability to approach
correct result.
|
Repeatability of measuring
process is called Precision
|
Your measurement will be close
to the standard measurement.
|
Your measurement will be
similar every time you measure.
|
Accuracy can be improved.
|
Precision cannot be improved.
|
Accuracy depends upon simple
techniques of analysis.
|
Precision depends upon many
factors like temperature etc.
|
Accuracy is necessary but not a
sufficient condition for precision.
|
Precision is necessary but not
a sufficient condition for accuracy.
|
Error
Every measured value
contains some uncertainty this uncertainty is called error.
Error = reading value - True value.
Note - It may be positive or
negative; but both has equal importance
Classification of error
→On the basis of nature of error
1. Systematic error - Systematic
error are those error that tend to be in one direction, either positive or
negative.
Some of causes
of systematic error are
a)
Instrumental error - Those errors which arise due to
imperfect designing of measuring instruments.
b)
Imperfect technique - Imperfection in experimental
technique or processor leads to systematic error.
c)
Personal error - These errors arise due to inexperience
of the observer. E.g- when we stand on the weighing scale; the reading goes
change when we tilt in any direction.
2. Random Error - These error
cause due to change in experimental condition which are out of control. E.g. - measurement
which are temperature dependent.
→ On the basis of mathematical calculations of measurement
1. Absolute Error - The difference between current reading
and average reading is called absolute error.
Note: In this case positive or negative sign is not considered.
2. Mean absolute error - Average of absolute error is called
mean absolute error.
3. Relative error /Fractional error - It is the ratio of
mean absolute error to average value or true value.
4. Percentage error - If the relative error is multiplied
with 100 then it is called percentage error.
You can easily understand these
four errors through this example. Suppose the time period of a S.H.M is 2.4s, 2.5s, 2.7s &
2.4s. Now see the table below
Significant figure/digit- The digit in a measurement which is trustworthy; are called significant figures
→ Rules for finding significant figure
(i)
Leading o's - insignificant
E.g.
0.054 km = 54 m
Here 0.0 is Insignificant.
(ii)
O’s bet two non-zero digit - significant
E.g. 1.012
Here all digits are significant.
(iii)
trailing o's
a)
Decimal point – significant
E.g. 0.230
Here last 0 is significant
b)
No decimal point – insignificant
E.g. 34000
Here last three 0 is insignificant (since we assumed as rounded off)
(iv)
All non 0’s digit is significant.